Color masterbatch is produced through a series of carefully controlled steps involving the mixing of base resins, pigments, and carrier resins, followed by extrusion, cooling, and pelletizing. Here's a detailed overview of the production process:
-
Weighing and Mixing: The process begins by precisely weighing the ingredients, including the base resin, pigments, and carrier resins. These materials are mixed together in specific proportions to ensure uniform color and compatibility. A mixer or compounder is used to achieve a consistent and homogeneous blend.
-
Extrusion: The blended mixture is fed into an extruder, where it is melted and processed under controlled temperature and pressure. The extrusion step breaks down pigment agglomerates and ensures an even distribution of pigments throughout the molten plastic.
-
Cooling and Pelletizing: After extrusion, the molten material is cooled, typically through a water bath or air cooling system, and then cut into small pellets. These pellets form the color masterbatch, which can later be used to color plastics during molding or extrusion processes.
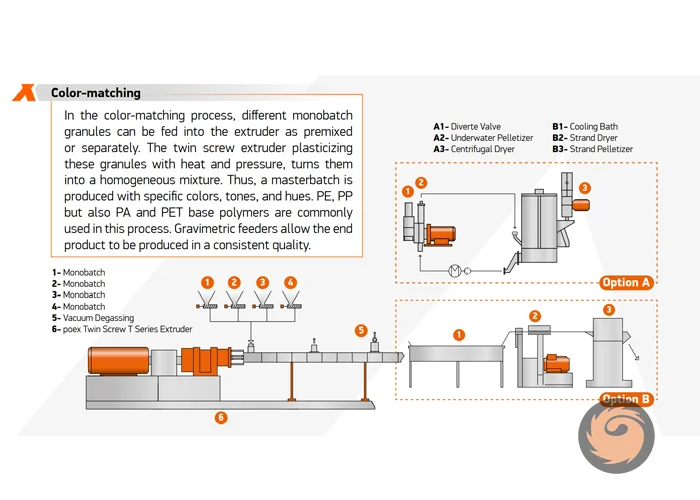
Additionally, the production process often involves a custom development phase where color engineers create specific masterbatch formulations based on customer requirements, including color matching using Pantone or RAL references, and testing the masterbatch in the customer's polymer to ensure the correct color and properties.
Key materials involved include:
-
Base Resin: The polymer that forms the bulk of the masterbatch.
-
Pigments: Provide the coloring effect.
-
Carrier Resin: Helps disperse the pigments evenly within the base polymer.
-
Additives: May be included for functionality like UV resistance or flame retardance.
The goal is to achieve a homogeneous dispersion of colorants within the polymer matrix, ensuring stable and consistent coloring of the final plastic products.
