-

What is antimicrobial masterbatch used for?
An antimicrobial masterbatch is used to give plastic products long-lasting protection against harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae, and certain viruses. It is a concentrated additive in a polymer carrier resin (like PE, PP, PS, ABS, etc.) that can be easily blended into plastic during processing. -

What is an antimicrobial masterbatch
An antimicrobial masterbatch is a concentrated formulation of antimicrobial additives and carrier resins that, when blended with base polymers, inhibit or reduce the growth of bacteria, fungi, algae, and other harmful microorganisms.It is widely used in plastic manufacturing to improve hygiene, durability, and product safety. By incorporating antimicrobial agents at the molecular level, masterbatches ensure long-lasting and consistent protection without compromising the appearance, texture, or strength of the final product. -
What is the difference between halogen and halogen-free flame retardant masterbatch?
The main difference is that halogen masterbatches contain halogens like bromine or chlorine, which work by releasing disruptive radicals to stop combustion but produce harmful gases and smoke. In contrast, halogen-free masterbatches avoid these elements, using alternatives like metal hydroxides to absorb heat and water or phosphorus compounds to create a char layer. Halogen-free options are generally considered safer for human health and the environment, generating less toxic smoke and corrosive fumes, and are increasingly replacing their halogenated counterparts, especially in sensitive applications. -
What are the types of flame retardant masterbatch
Flame retardant masterbatches are primarily classified as either halogenated or non-halogenated. Halogenated types use bromine or chlorine compounds to inhibit flames, while non-halogenated types include phosphorus-based, metal hydroxide, melamine-based, and nitrogen-based flame retardants that act by forming char, releasing heat, or creating non-flammable gases. The choice between them depends on the application, regulatory requirements, and desired flame retardancy performance. -

How does flame retardant masterbatch work in plastics?
Flame retardant masterbatch works by adding chemicals to plastic that interfere with the combustion process. These chemicals act in one of four ways: by cooling the material (endothermic reaction and release of water), by forming a protective char layer that acts as a barrier to oxygen and heat, by releasing inert gases (like hydrogen halide gas) that dilute oxygen and suppress flames, or by chemically interfering with the gaseous phase reactions necessary for fire to spread. These mechanisms slow down or stop the spread of fire, helping plastic products meet safety standards. -

What is a flame retardant additive masterbatch
A flame retardant additive masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of flame retardant additives blended into a carrier resin, designed to be added to polymers (like plastics or rubber) to make them more resistant to fire. This additive masterbatch improves fire safety by reducing flammability, slowing the spread of fire, and suppressing smoke formation in the final product. -
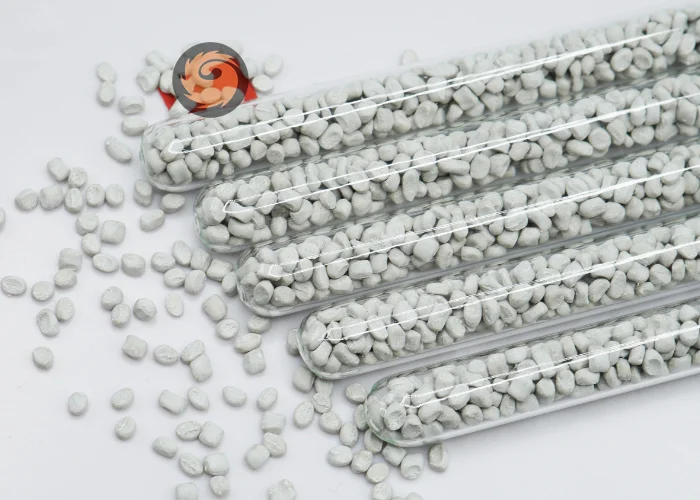

What polymers are compatible with antioxidant masterbatches
These masterbatches are compatible with a wide range of thermoplastic polymers, including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA, Nylon), polycarbonate (PC), and polyoxymethylene (POM). Specialty polymers such as PVC, TPU, and engineering blends can also benefit from antioxidant protection when high thermal stability or UV resistance is required. -
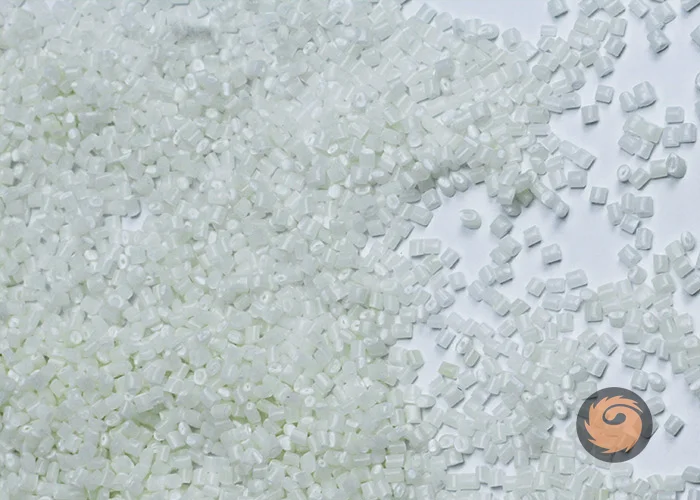

Which carriers are used in anti-oxidant masterbatch?
the Anti-oxidant masterbatch common carriers include polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE), polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, and high-performance engineering polymers like PET, PC, and PA. -
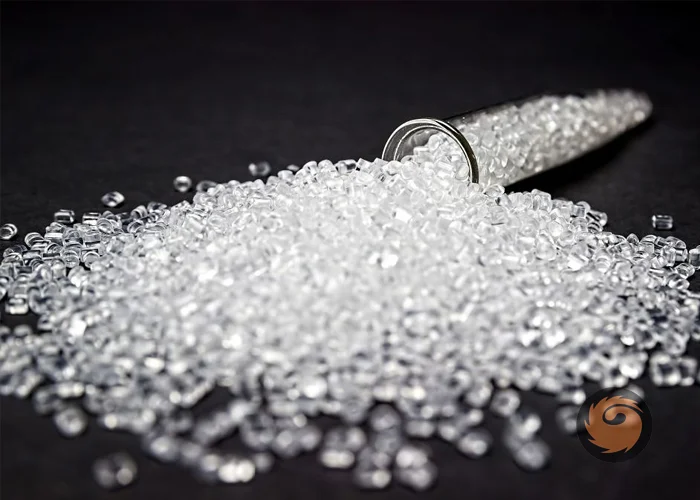

What is an anti-oxidant masterbatch
Anti-oxidant masterbatch are essential additives in the polymer and plastics industry, designed to protect materials from thermal and oxidative degradation. By incorporating concentrated antioxidants into a compatible carrier, these masterbatches ensure that polymers maintain their mechanical properties, appearance, and longevity both during processing and throughout their service life. -
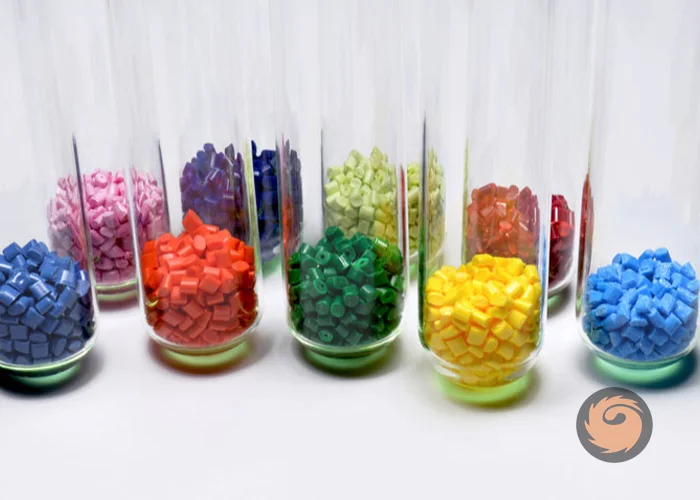

How does additive masterbatch differ from colour masterbatch
additive masterbatch is used to enhance or modify the functional properties of plastics, such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, anti-static, or anti-fog effects, while colour masterbatch is primarily designed to provide consistent coloration and aesthetic appeal by dispersing pigments or dyes in the polymer. In short, additive masterbatch focuses on performance improvement, whereas colour masterbatch focuses on appearance. -
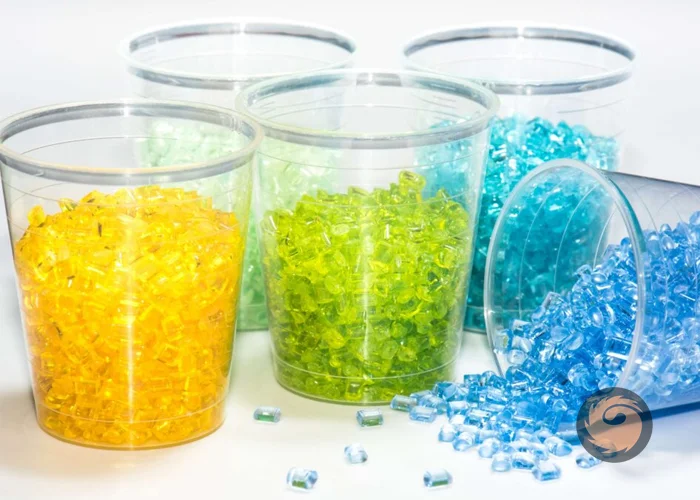

What are additive masterbatch
Unlike color masterbatch, which primarily adds color, additive masterbatch enhances or modifies the physical and chemical properties of plastic products to improve their functionality, performance, or processing characteristics. -
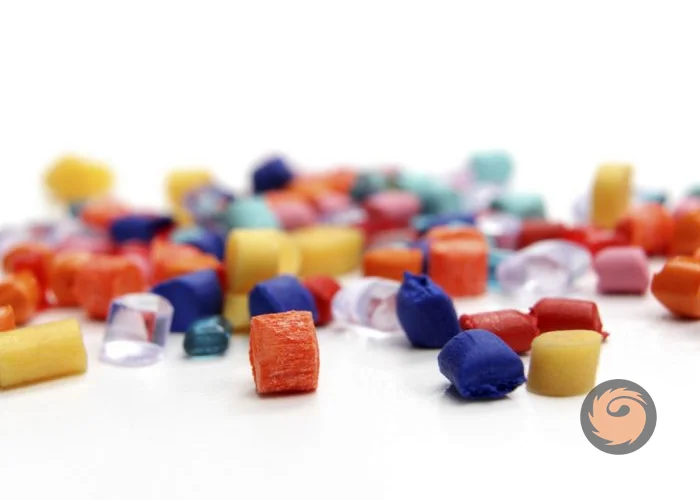

What is ABS masterbatch used for?
ABS masterbatch is a convenient way to color, enhance, and modify ABS plastic while ensuring consistent quality in the final product. -
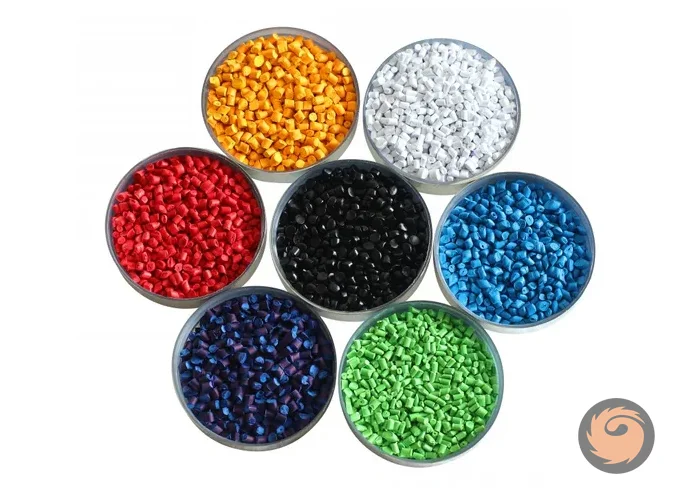

What is the difference between white, black, and colored masterbatch?
White, black, and colored masterbatches differ in pigment composition and applications: white uses titanium dioxide for brightness and UV protection, black contains carbon black for deep color and durability, and colored masterbatches offer customizable shades for vibrant plastic products. Each type is tailored to meet specific aesthetic and functional needs in plastic manufacturing. -
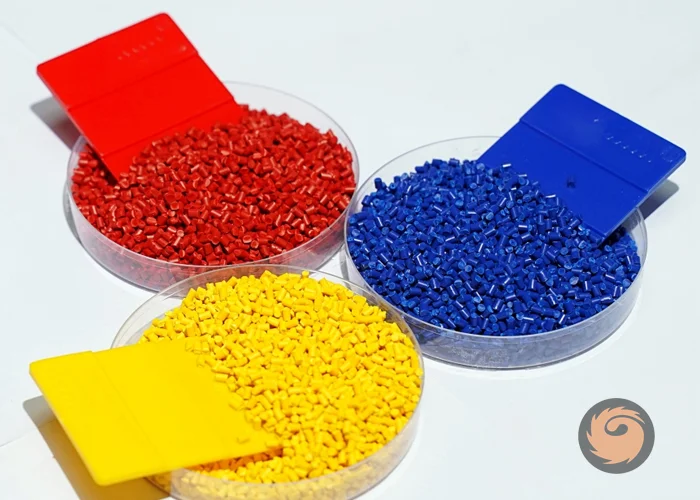

What is plastic color masterbatch?
Plastic color masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of pigments or dyes dispersed in a polymeric carrier resin. It is used to add vibrant and uniform color to plastic products during the manufacturing process. The masterbatch is typically composed of a carrier resin compatible with the base plastic (such as polyethylene or polypropylene) and a high concentration of colorants, usually ranging from 20% to 50%. This formulation allows manufacturers to produce plastics in a wide range of colors with consistent color distribution. -
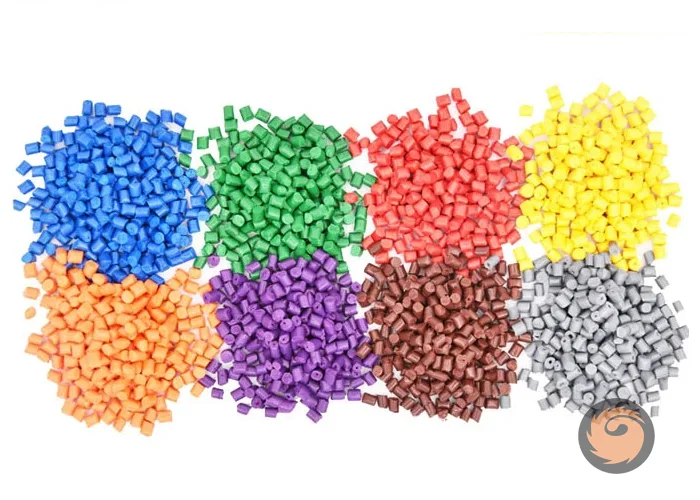

How do you choose the right PP color masterbatch?
the right PP color masterbatch is one that is compatible with polypropylene, offers accurate and consistent color, can withstand processing conditions and environmental exposure, uses high-quality pigments, and comes from a reliable supplier with good support and quality control. -
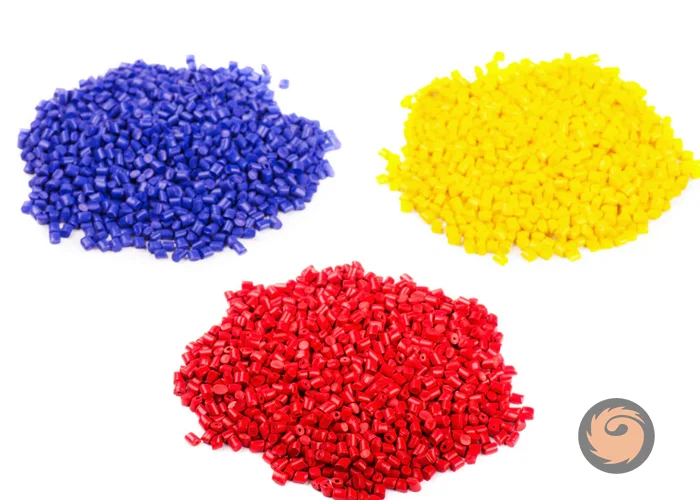

What is PP color masterbatch used for?
PP color masterbatch's main role is to uniformly color polypropylene plastic products while improving processing efficiency and reducing costs during manufacturing.Common applications include injection molding and extrusion processes to manufacture colored plastic items such as boxes, containers, chairs, crates, buckets, battery cases, and hangers. -
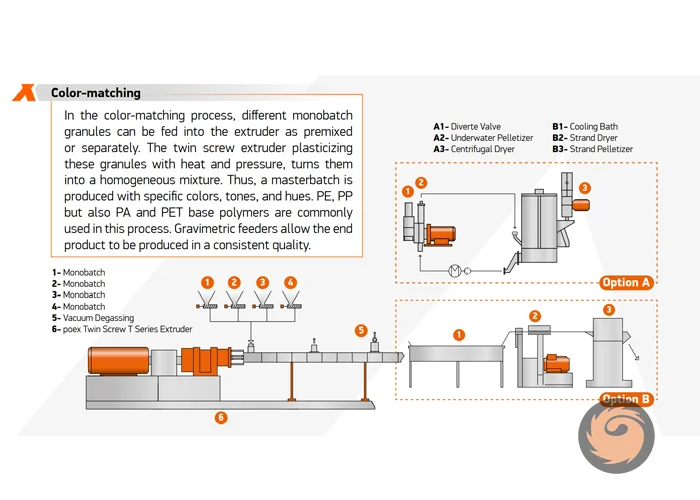
How is color masterbatch produced?
Color masterbatch is produced through a series of carefully controlled steps involving the mixing of base resins, pigments, and carrier resins, followed by extrusion, cooling, and pelletizing. -
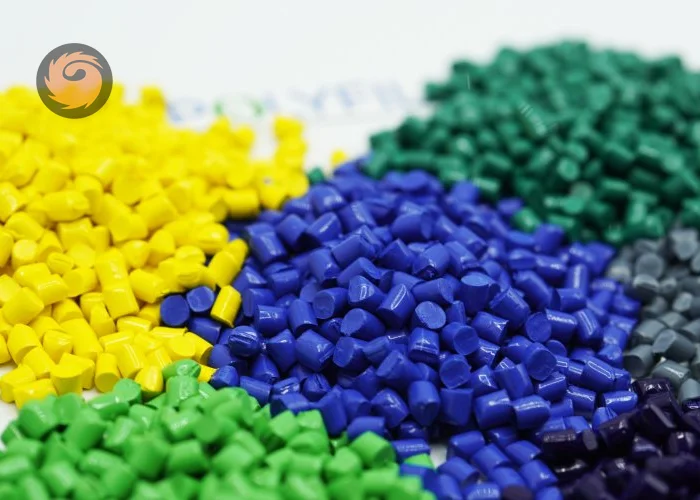

What is color masterbatch for polymers?
Color masterbatch for polymers is a concentrated mixture of pigments or dyes dispersed in a polymer carrier resin, designed to add color to plastic products during the manufacturing process. Instead of adding pure pigments directly (which are difficult to handle and disperse evenly), manufacturers use color masterbatch in pellet, granule, or liquid form.

